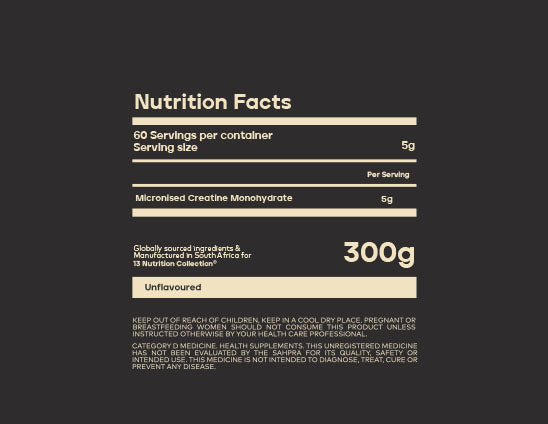
13 Nutrition
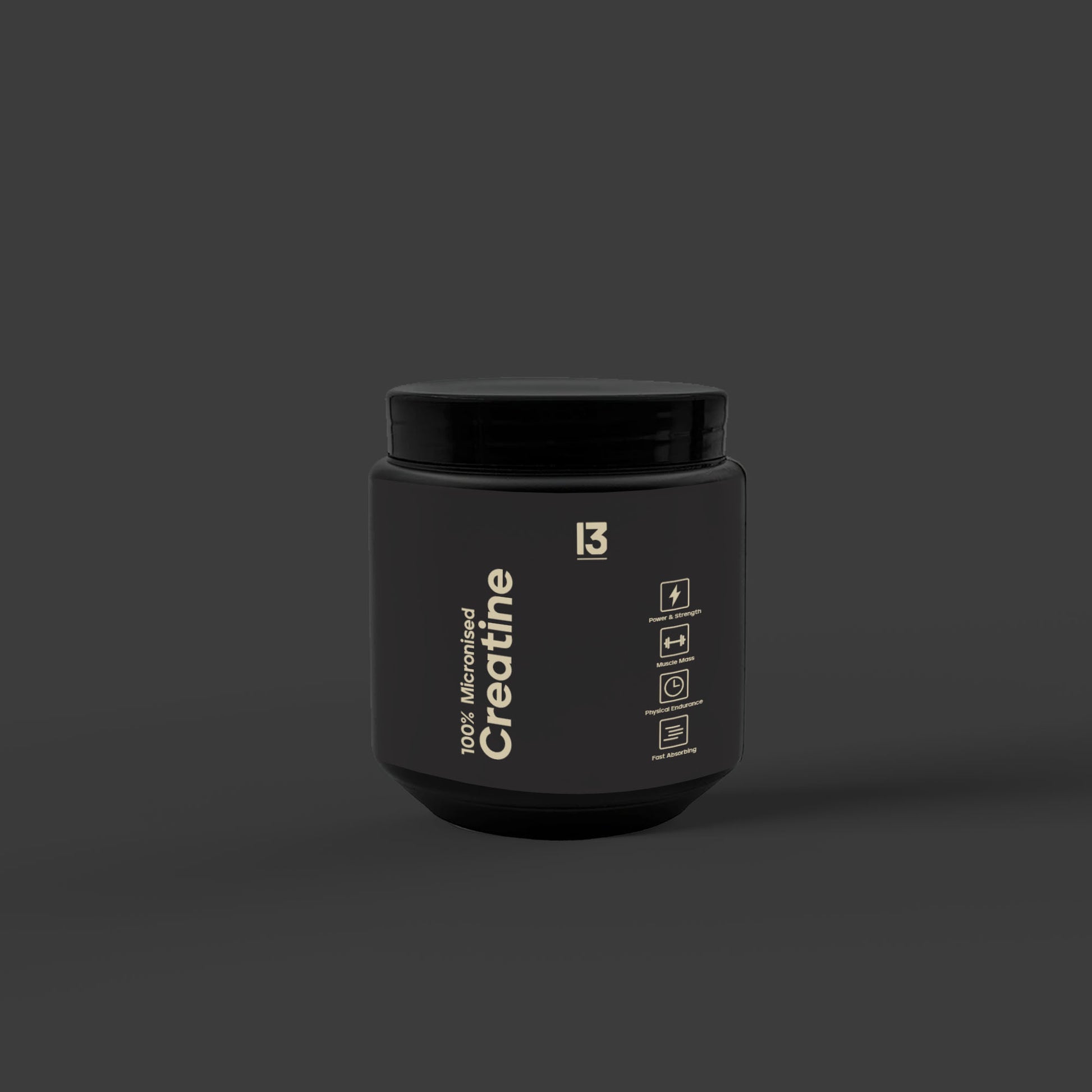
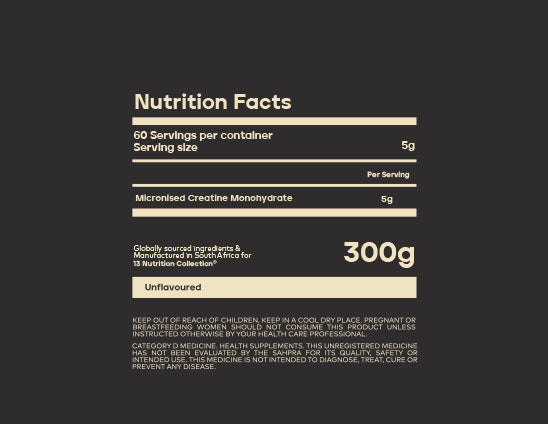
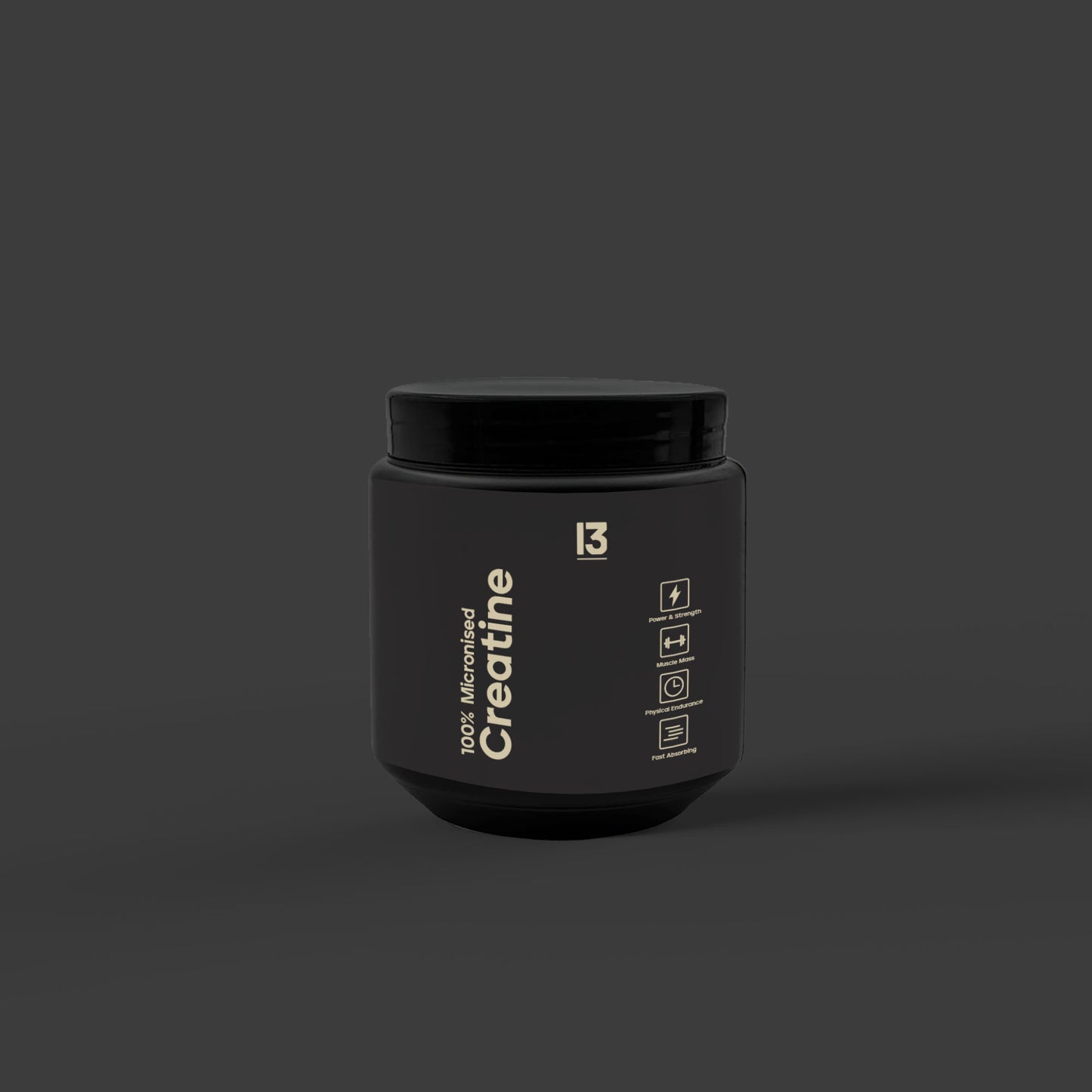
13 100% Micronised Creatine
13 100% Micronised Creatine
200 MESH MICRONISED CREATINE MONOHYDRATE.
 Increased Muscle Building
Increased Muscle Building
 Explosive Energy & Focus
Explosive Energy & Focus
 5g Daily for Life
5g Daily for Life
 Tested 99.9% Purity.
Tested 99.9% Purity.
 Triple Filtered.
Triple Filtered.
 Clean, Safe, and Highly Bioavailable.
Clean, Safe, and Highly Bioavailable.
Pure Quality. Pure Results.The extensive studies on creatine monohydrate have consistently demonstrated its effectiveness in promoting muscle size, strength, and recovery when used in conjunction with a well-balanced diet and regular weight training.60 PURE SERVINGS PER TUB.
Couldn't load pickup availability
What's Inside
What's Inside
300g of Pure Micronised Creatine Monohydrate
- 5g scoop inside
- 60 servings
- That's it.. Pure, Clean & Simple.
Texture & Taste
Texture & Taste
13 100% Micronised Creatine is 40 times finer then your normal Creatine Monohydrate.
This means it dissolves instantly into liquid & has no flavour.
Instructions
Instructions
Take 1 serving (5g) everyday!
It's unflavoured, so add it your 13 Hydrating Electrolytes during a workout, or pop it in your protein shake after a workout.
289 in stock
View full details

-
Power & Strength
Creatine helps with power and strength by increasing the body's stores of creatine phosphate, a form of stored energy in muscles. This leads to several mechanisms that enhance power and strength:
- Increased ATP Production
- Enhanced Recovery
- Muscle Fiber Recruitment
These effects contribute to better performance in short-term, high-intensity activities.
-
Muscle Mass
Creatine supports muscle mass growth through several mechanisms:
- Cell Hydration
- Increased Energy
- Improved Performance
- Training Capacity
- Muscle Fiber Recruitment
- Anabolic Effects
To maximize muscle growth, combine creatine with appropriate strength training and a balanced diet.
-

Physical Endurance
Creatine's main benefits are typically seen in short, high-intensity activities rather than endurance exercises. However, it might indirectly aid endurance by:
- Faster Recovery
- Enhanced Muscle Function
- Potential Ergogenic Effects
-
Fast Absorbing
Fast absorption of creatine is important because it allows the compound to reach the muscles quickly and be readily available for use during high-intensity, short-duration activities. Here are some reasons why fast absorption is important for creatine:
- Immediate Energy Production
- Enhanced Performance
- Optimal Muscle Volumization
- Reduced Fatigue
WHY DO YOU EVEN NEED IT
The Why
Why Do You Need 13 Micronised Creatine ?
While the human body naturally produces creatine and can obtain some from dietary sources, there are several reasons why individuals may choose to supplement with extra creatine:
- Enhanced Exercise Performance: Creatine supplementation can provide additional energy for high-intensity, short-duration activities. This extra energy allows for improved exercise performance in sports like weightlifting, sprinting, and powerlifting, which rely on immediate energy sources.
- Increased Muscle Mass: Creatine may promote muscle growth by enhancing muscle cell volumization and supporting protein synthesis. This can be beneficial for individuals, especially athletes, looking to increase their muscle mass and strength.
- Faster Recovery: Creatine can reduce post-exercise fatigue and improve recovery between sets and workouts. This can lead to increased training volume and more efficient progress over time.
- Improved Muscle Function: By maintaining muscle power and strength, creatine can help delay the onset of fatigue, potentially leading to better performance during physical activities.
- Cognitive Benefits: Some studies suggest that creatine supplementation may have cognitive benefits, such as improved memory and mental clarity, which can be of interest to individuals seeking mental and physical performance improvements.
- Support for Vegetarians and Vegans: Creatine is naturally found in animal products, so vegetarians and vegans may have lower natural creatine levels. Supplementing with creatine can help compensate for this deficiency.
Should Woman Use Creatine?
Creatine is a widely researched supplement primarily known for its ability to enhance athletic performance, muscle strength, and muscle mass gains. While it's commonly associated with male athletes or bodybuilders, creatine can also benefit women who are involved in resistance training or high-intensity activities. Here are some reasons why women might consider using creatine:
- Increased Strength and Exercise Performance: Creatine helps in the production of ATP, which is the primary energy currency in the body. By increasing the availability of ATP, creatine supplementation can lead to improved strength, power, and exercise performance. This can be beneficial for women participating in activities requiring bursts of energy, such as weightlifting, HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training), or sprinting.
- Muscle Growth: While women might have different goals than men when it comes to muscle growth, creatine can still aid in muscle growth and recovery. It helps in increasing lean muscle mass, which can be valuable for anyone looking to enhance their muscle tone and metabolism.
- Improved Recovery: Creatine supplementation can potentially help in reducing muscle damage and inflammation, leading to faster recovery after intense workouts. This is particularly useful for women engaged in regular exercise routines.
- Cognitive Benefits: Some research suggests that creatine might have cognitive benefits, such as improved memory and reasoning skills. This can be advantageous for women who are looking to enhance their cognitive function along with their physical performance.
It's essential to note that while creatine can be advantageous for many, individual responses can vary. Always consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before starting any supplementation, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or concerns.
Additionally, ensuring proper hydration while taking creatine is crucial as it can cause water retention in muscles.
What's actually inside
The What
So What is Creatine Precisely?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in small amounts in certain foods and synthesized in the human body, primarily in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. It plays a crucial role in the body's energy production system, particularly during short bursts of high-intensity activities. Here's a more precise explanation of creatine:
- Chemical Composition: Creatine is a nitrogenous organic acid that is composed of three amino acids: arginine, glycine, and methionine. It is a molecule with a chemical formula of C4H9N3O2.
- Energy Production: Creatine is stored in the muscles in the form of creatine phosphate. During intense physical activities, such as weightlifting or sprinting, the body rapidly converts creatine phosphate into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary energy source for muscle contractions. This quick energy release aids in short bursts of power and strength.
- Dietary Sources: Small amounts of creatine can be obtained from dietary sources, primarily from red meat and seafood. However, the amount of creatine that can be consumed through a typical diet is relatively low compared to what can be obtained through supplementation.
- Supplementation: Due to its performance-enhancing benefits, creatine is commonly used as a dietary supplement. Creatine supplements come in various forms, with creatine monohydrate being the most researched and widely used. When taken as a supplement, creatine can increase the body's creatine phosphate stores, enhancing the ability to produce ATP and, in turn, improving strength and power during high-intensity exercise.
Creatine has been extensively studied and is considered safe for most people when used as directed. It is particularly popular among athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals engaging in high-intensity training, but it can be beneficial for anyone looking to improve their exercise performance and muscle-related goals.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation, especially if you have specific health concerns or conditions.
Creatine Myth Busters: 4 things we've all heard before...
Loading Phase Clarification:
Myth: Creatine Loading Isn't Necessary.
Fact: Loading Decreases Time for Full Muscle Cell Saturation.
Loading accelerates saturation of muscle cells, reducing the time it takes to reach maximum creatine levels.
Hair Loss Concern:
Myth: Creatine Causes Hair Loss.
Fact: No Scientific Evidence Supports Hair Loss Claim.
Scientific studies have not found evidence linking creatine supplementation to hair loss.
Water Retention Debunked:
Myth: Creatine Causes Water Retention.
Fact: Initial Water Retention, but No Long-Term Effects.
Short-term water retention occurs due to increased intracellular volume but doesn't cause prolonged water retention.
Kidney Damage Misconception:
Myth: Creatine Causes Kidney Damage.
Fact: No Impact on Kidney Function in Healthy Individuals.
Scientific evidence shows no adverse impact on kidney function in healthy individuals.
Scientific Evidence and Conclusion:
Numerous myths surrounding creatine lack scientific support.
Scientific evaluation supports the safety and benefits of creatine supplementation for enhancing athletic performance and muscle function.
Debunking these myths reveals the beneficial aspects of creatine backed by research and evidence.
The How
The How?
How Does Creatine Increase Power & Strength?
Creatine helps with power and strength by increasing the body's stores of creatine phosphate, a form of stored energy in muscles. This leads to several mechanisms that enhance power and strength:
- Increased ATP Production: Creatine speeds up the production of ATP, which is essential for muscle contractions during high-intensity activities like weightlifting and sprinting.
- Enhanced Recovery: Creatine may support faster post-exercise recovery, allowing for increased training volume and intensity over time.
- Muscle Fiber Recruitment: Creatine might improve the recruitment of fast-twitch muscle fibers, which are crucial for generating force and power.
These effects contribute to better performance in short-term, high-intensity activities.
How does Creatine help build Muscle?
Creatine supports muscle mass growth through several mechanisms:
- Cell Hydration: It draws water into muscle cells, promoting an environment for muscle protein synthesis.
- Increased Energy: Creatine provides extra energy for high-intensity workouts, leading to more muscle stimulation.
- Improved Performance: It enhances strength training performance, contributing to muscle gains.
- Training Capacity: Creatine reduces fatigue and aids recovery, allowing for increased training volume and muscle growth.
- Muscle Fiber Recruitment: It may enhance the recruitment of muscle fibers important for force generation.
- Anabolic Effects: Some studies suggest creatine may directly influence muscle protein synthesis.
To maximize muscle growth, combine creatine with appropriate strength training and a balanced diet.
How does Creatine help me with Endurance?
Creatine's main benefits are typically seen in short, high-intensity activities rather than endurance exercises. However, it might indirectly aid endurance by:
- Faster Recovery: Helping reduce post-exercise fatigue and aiding quicker recovery between intense bouts of exercise.
- Enhanced Muscle Function: Supporting muscle power and strength, potentially delaying fatigue onset during endurance activities.
- Potential Ergogenic Effects: Some research suggests modest benefits for endurance in terms of time to exhaustion, exercise economy, and overall capacity.
How does Fast Absorbtion help Performance?
Fast absorption of creatine is important because it allows the compound to reach the muscles quickly and be readily available for use during high-intensity, short-duration activities. Here are some reasons why fast absorption is important for creatine:
- Immediate Energy Production: Fast absorption ensures that creatine is readily available to support ATP regeneration right when it's needed.
- Enhanced Performance: During short bursts of maximal effort, having an immediate source of energy can lead to improved exercise performance.
- Optimal Muscle Volumization: Quick absorption allows creatine to draw water into muscle cells, promoting cell volumization. This process can create an environment conducive to muscle growth and improve overall muscle function.
- Reduced Fatigue: Rapid absorption means that creatine can begin replenishing ATP stores sooner, potentially reducing fatigue and allowing athletes to perform at their best for longer periods during high-intensity activities.